[LLM] over «Michael Hudson: Trump on Greenland, Panama and Canada»
Tabular, visual, and textual breakdowns and summaries
Introduction
This post applies various Large Language Model (LLM) summarization prompts to the transcript of the program «Michael Hudson: Trump on Greenland, Panama and Canada» by the YouTube channel Dialogue Works.
In the program, Michael Hudson discusses Donald Trump's foreign policy strategies, particularly focusing on Greenland and Canada. He critiques Trump's transactional approach, emphasizing threats over diplomatic incentives. Hudson highlights the broader implications of U.S. economic and geopolitical maneuvers, including their effects on Europe, NATO, and global trade dynamics.
Here is a table of themes discussed in the text:
Remark: The LLM results below were obtained from the "raw" transcript, which did not have punctuation.
Remark: The transcription software had problems parsing the names of mentioned people and locations. Some of the names were manually corrected.
Post’s structure:
Most important or provocative statements
Extending the summary.Mind-map
For orientation.Summary, ideas, and recommendations
The main course.Hidden and propaganda messages
Didactic POV.Sophisticated feedback
While wearing hats of different colors.
Most important or provocative statements
Here is a table of the most important or provocative statements in the text:
Donald Trump's Policy on Greenland
Trump claims Greenland is needed for national security and suggests Denmark should give it up.
He implies economic force, such as tariffs, could be used against Denmark if they don't comply.
The strategy is likened to historical U.S. tactics of using perceived threats to justify actions.
U.S. Economic and Military Strategy
Trump's approach is described as "we win, you lose," focusing on economic threats rather than military force.
The U.S. aims to control global resources and trade routes, such as the North Atlantic and Arctic sea lanes.
There is a focus on using economic leverage to achieve U.S. goals without offering positive incentives to other countries.
Impact on Europe and NATO
Trump is seen as using Greenland as a wedge to influence European NATO members.
The U.S. is pushing for increased military spending from NATO countries, threatening to withdraw if demands are not met.
European countries face a political and economic crisis due to U.S. pressures and the threat of tariffs.
U.S. Relations with Canada and Mexico
The U.S. has historically exploited Canadian resources and industry, with current threats of tariffs causing economic strain.
Mexico's new political direction poses a challenge to U.S. influence, with potential shifts towards self-sufficiency and independence.
Global Economic Influence and BRICS
The U.S. is seen as creating chaos to maintain control, while BRICS is growing as an alternative power bloc.
American policy is criticized for focusing on short-term gains at the expense of long-term stability.
The lack of a cohesive alternative model from other countries allows the U.S. to maintain its influence.
Panama Canal and Global Trade Routes
Trump suggests China controls the Panama Canal, though this is refuted as a misinterpretation of China's port developments.
The U.S. seeks to control choke points like the Panama Canal to exert influence over global trade.
Overall U.S. Foreign Policy Strategy
The U.S. aims to prevent other countries from developing alternatives to its economic and political dominance.
There is a focus on maintaining control over resources and trade routes to ensure U.S. global influence.
The rest of the world is criticized for lacking a cohesive strategy to counter U.S. dominance.
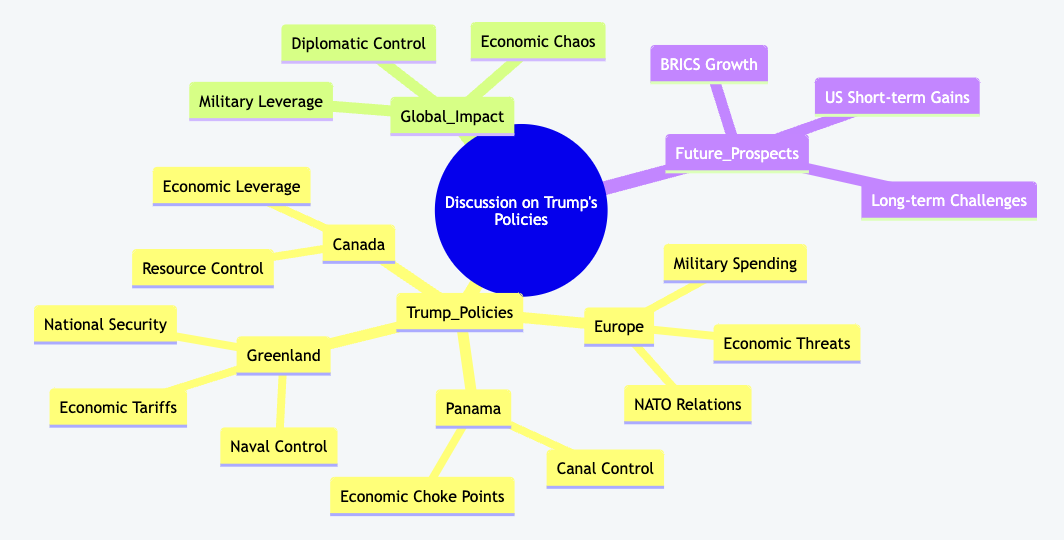
Mind-map
Here is a mind-map summarizing the text:
Summary, ideas, and recommendations
SUMMARY
Michael Hudson discusses Donald Trump's foreign policy strategies, particularly focusing on Greenland and Canada. He critiques Trump's transactional approach, emphasizing threats over diplomatic incentives. Hudson highlights the broader implications of U.S. economic and geopolitical maneuvers, including their effects on Europe, NATO, and global trade dynamics.
IDEAS
Trump's interest in Greenland is driven by strategic military and economic advantages.
The U.S. uses economic threats, like tariffs, as leverage in international relations.
Greenland's strategic location offers control over North Atlantic and Arctic sea lanes.
Trump's approach mirrors historical U.S. tactics in Iceland and other regions.
The U.S. aims to economically control Europe through NATO and EU mechanisms.
Trump's policies are seen as short-term, prioritizing immediate gains over long-term stability.
American foreign policy heavily relies on creating economic and trade chaos.
The U.S. seeks to maintain global dominance without direct military intervention.
European countries face internal political crises due to U.S. pressures.
The U.S. aims to disrupt global trade routes, like the Panama Canal, for strategic control.
Mexico's potential independence from U.S. economic influence is a concern for Trump.
The U.S. uses "choke points" in trade and energy to exert international influence.
America's economic colonialism contrasts with its historical military colonialism.
The BRICS nations are emerging as a counterbalance to U.S. dominance.
The U.S. seeks to prevent other countries from developing independent economic policies.
Trump's transactional diplomacy emphasizes threats over mutual benefits.
The U.S. aims to maintain control over global financial systems.
Trump's policies may lead to long-term isolation for the U.S.
The U.S. leverages NATO to centralize arms negotiations and control European spending.
The U.S. strategy involves maintaining chaos to prevent other nations from self-sufficiency.
QUOTES
"We need Greenland for national security purposes."
"Trump's basic policy is we win, you lose."
"America can control the world economically by making economic threats."
"Trump is using Greenland as a wedge into Europe for NATO."
"America's role as a chaos creator."
"The U.S. wants to control the whole world economically."
"Trump's transactional approach of any deal that's made."
"America is not the most efficient economy; it's de-industrialized."
"The U.S. aims to prevent other countries from having a choice."
"The rest of the world is living in a state of chaos."
"The U.S. uses 'choke points' to disrupt traditional trade patterns."
"Mexico could become a new America."
"The U.S. wants to cut up the whole world into parts."
"America's foreign policy is to prevent other countries from having a choice."
"There's a lack of the rest of the world acting in its self-interest."
HABITS
Engaging in transactional diplomacy focused on threats.
Prioritizing short-term gains over long-term stability.
Utilizing economic leverage over military intervention.
Creating chaos as a strategic tool in international relations.
Focusing on controlling global trade routes and financial systems.
FACTS
Greenland has strategic military and economic importance for the U.S.
The U.S. uses tariffs as a primary tool for international leverage.
NATO is used by the U.S. to centralize arms negotiations in Europe.
The Panama Canal is a strategic choke point for global trade.
The BRICS nations are becoming a significant counterbalance to U.S. influence.
Mexico's economy was significantly impacted by NAFTA.
The U.S. aims to maintain economic dominance without direct military control.
European countries face political crises due to U.S. economic pressures.
Water scarcity is becoming a significant global issue, potentially more valuable than oil.
REFERENCES
Financial Times
The Wall Street Journal
NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement)
BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa)
NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization)
RECOMMENDATIONS
Countries should develop independent economic policies to counter U.S. influence.
European nations need to consider alternatives to NATO's centralized arms control.
Nations should explore self-sufficiency to reduce reliance on U.S. economic systems.
Developing a "Plan B" for trade and financial systems is crucial for global stability.
Countries should focus on mutual aid and cooperation to counteract U.S. dominance.
Emphasizing long-term strategies over short-term gains can lead to sustainable growth.
Exploring alternative trade routes and partnerships can reduce dependency on U.S. systems.
Nations should consider the implications of U.S. "choke points" in global trade.
Developing local industries and agriculture can enhance national self-sufficiency.
Exploring alliances with BRICS nations can provide a counterbalance to U.S. influence.
Hidden and propaganda messages
In this section we try to find is the text apolitical and propaganda-free.
Remark: We leave to the reader as an exercise to verify that both the overt and hidden messages found by the LLM below are explicitly stated in the text.
Remark: The LLM prompt "FindPropagandaMessage" has an explicit instruction to say that it is intentionally cynical. It is also, marked as being "For fun."
The LLM result is rendered below.
OVERT MESSAGE
Trump's Greenland policy aims to strengthen U.S. national security and global strategic interests.
HIDDEN MESSAGE
Trump's Greenland policy is a strategic move for economic dominance and geopolitical leverage.
HIDDEN OPINIONS
America should use economic threats to control global resources and territories.
U.S. foreign policy relies on creating chaos for strategic advantage.
Greenland's resources are essential for U.S. geopolitical dominance.
Economic leverage is more effective than military force for U.S. control.
National security is a guise for expanding U.S. economic influence.
U.S. aims to weaken European unity through strategic economic maneuvers.
American foreign policy prioritizes economic gains over international cooperation.
U.S. seeks to maintain global dominance by exploiting economic vulnerabilities.
Trump's policies reflect a transactional approach to international relations.
U.S. uses NATO as a tool for enforcing American economic interests.
Economic threats are the primary tool for U.S. foreign policy.
U.S. aims to destabilize global trade to maintain economic superiority.
Trump views international relations as zero-sum transactions.
U.S. seeks to control global trade routes for strategic advantage.
American policies aim to isolate potential economic competitors.
U.S. foreign policy undermines allies to ensure American supremacy.
SUPPORTING ARGUMENTS AND QUOTES
Trump's focus on Greenland's resources indicates a desire for economic control.
"We need Greenland for national security purposes" masks economic motivations.
Trump's tariffs on Denmark highlight economic leverage over military force.
The comparison to Iraq war propaganda suggests manipulation of public opinion.
"We win, you lose" reflects a transactional approach to international relations.
Trump's policies mirror historical colonialist strategies for resource acquisition.
The emphasis on NATO spending suggests economic coercion of allies.
Trump's rhetoric on Greenland aligns with broader U.S. economic strategies.
The focus on economic threats indicates a shift from military to economic dominance.
Trump's policy is consistent with historical U.S. strategies of economic imperialism.
DESIRED AUDIENCE OPINION CHANGE
Accept U.S. economic dominance as necessary for national security.
View economic threats as legitimate tools in foreign policy.
Support U.S. expansion into strategic territories like Greenland.
Believe in the necessity of American control over global resources.
Accept transactional diplomacy as standard international practice.
View NATO as a tool for U.S. economic interests.
Support U.S. economic strategies over military interventions.
Accept economic chaos as a strategic tool for U.S. dominance.
Trust U.S. leadership in global economic matters.
View international relations as zero-sum transactions.
DESIRED AUDIENCE ACTION CHANGE
Support U.S. policies that prioritize economic leverage over military force.
Advocate for increased U.S. control over global trade routes.
Endorse U.S. economic dominance as a national security measure.
Support tariffs and economic sanctions as foreign policy tools.
Advocate for U.S. expansion into resource-rich territories.
Support NATO spending aligned with U.S. economic interests.
Endorse U.S. policies that destabilize global competitors.
Advocate for U.S. control over strategic global resources.
Support transactional diplomacy in international relations.
Endorse U.S. economic strategies that undermine global competitors.
MESSAGES
Michael Hudson wants you to believe he is discussing Greenland's strategic importance, but he is actually highlighting U.S. economic imperialism.
PERCEPTIONS
Michael Hudson wants you to believe he is a geopolitical analyst, but he's actually critiquing U.S. economic dominance strategies.
ELLUL'S ANALYSIS
According to Jacques Ellul's analysis, the discussion of Trump's Greenland policy reflects the use of propaganda to shape public perception of national security as a justification for economic imperialism. The narrative leverages fear of foreign threats to garner domestic support for strategic economic maneuvers, illustrating Ellul's concept of integrating propaganda with political objectives.
BERNAYS' ANALYSIS
Edward Bernays would interpret the discourse as a classic example of engineering consent through strategic messaging. By framing Greenland as vital for national security, the narrative manipulates public opinion to support economic expansion under the guise of protection. This aligns with Bernays' view of propaganda as a tool for shaping public attitudes to align with elite interests.
LIPPMANN'S ANALYSIS
Walter Lippmann's analysis would suggest that the narrative around Greenland exemplifies the manufacturing of public consent through simplified messaging. By reducing complex geopolitical strategies to national security concerns, the discourse creates a distorted public perception that aligns with elite economic interests, reflecting Lippmann's critique of media-driven public opinion.
FRANKFURT'S ANALYSIS
Harry G. Frankfurt would critique the narrative as an exercise in strategic misrepresentation, or "bullshit," where the truth is secondary to advancing political and economic agendas. The focus on national security as a justification for economic expansion exemplifies the manipulation of facts to serve power structures, aligning with Frankfurt's analysis of deceptive communication.
NOTE: This AI is tuned specifically to be cynical and politically-minded. Don't take it as perfect. Run it multiple times and/or go consume the original input to get a second opinion.
Sophisticated feedback
In this section we try to give feedback and ideas while wearing different hats. Like "black hat", "white hat", etc.
The LLM result is rendered below.
Summary of the Idea
The discussion revolves around Donald Trump's interest in acquiring Greenland for national security purposes. The conversation touches on the geopolitical implications of such a move, including the potential benefits for the U.S. in terms of controlling strategic sea lanes and natural resources. The dialogue also explores the broader context of U.S. foreign policy under Trump, characterized by economic leverage and transactional diplomacy. The conversation highlights the potential consequences for Europe and other regions, as well as the skepticism surrounding Trump's intentions and the feasibility of his plans.